Boils Types Symptoms Causes Treatment & Preventions
Boil (or boils) is a skin infection in which pus-filled vesicles appear on the skin surface. Generally, this condition persists in the hair follicles and is also called folliculitis or furuncle.
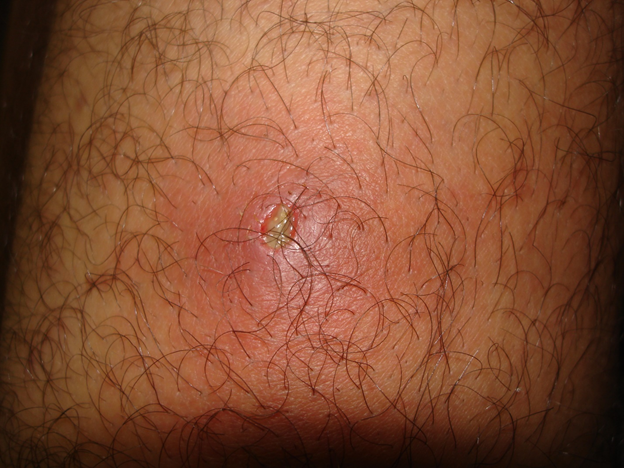
A boil is a bacterial infection, and the causative agent is a bacterium called Staphylococcus aureus. It shares many properties with acne (a type of skin infection) and can be infectious in some people.
A boil or skin abscess (accumulation of pus) can indicate disorders like fever or diseases like cancer. They can also be prompted if you are taking immune-suppressor medications.
Boils are not related to poor hygiene or skincare of a person but they can spread from person to person. As these are not entirely preventable, treatment usually focuses on reducing the chances of infection.
Types of Boils:
Among many types of boils, some are given below:
· Carbuncle:
A carbuncle is a cluster of boils. This infection is characterized by the presence of more than one boils at one place, connected. Carbuncles are usually bacterial infections and can be contagious.
· Hidradenitis suppurativa:
It is a skin infection in which small painful, fluid-filled lumps appear under the skin. These lumps are usually present in the area where the skin touches itself, like armpits, buttocks, and breasts. The exact mechanism of hidradenitis suppurativa is unknown. However, they occur near the hair-rich areas.
· Intraoral dental sinus:
A boil that appears on the gums is called an intraoral dental sinus. It is a mouth lesion that is characterized by red, painful, and swollen spots at the gums. It is also called gumboil or parulis and can lead to the removal of infected teeth or gum.
· Sty:
A sty or stye is a red bump on the skin, filled with pus. It most commonly appears near the eyelashes or inside the eyelid. Styes are also indications of a bacterial infection. They are frequent in the areas where oil-producing glands are present (in the base of the eyes).
Location of Boils:
Boils usually appear in the hair-rich areas or the areas where the production of oil is in excess. They can be found on any part of the body. The most favorite places of the boils are:
- Neck
- Groin
- Armpits
- Buttocks
- Shoulders
Causes of Boils:
The causes of the boils are as follow:
· Staphylococci bacteria:
The most common cause of boils is a bacterial infection that involves Staphylococcus aureus. This bacterium is responsible for many respiratory tracts and skin infections.
· Genetics:
Boils also travel in the family tree and can infect more than one person of the same family.
· Contact with an already infected person:
Avoid a person if he has a staph infection. Bacterial infections are contagious and can spread from person to person.
· Immunocompromised patient:
If a person has a weaker immune system or is taking immunosuppressants, he is more susceptible to developing boils.
The diseases like diabetes, cancer, obesity, and hematological disorders are also causative agents for boils as these diseases suppress immunity.
Signs and Symptoms of Boils:
Infection of boil starts from a small, red lump that sizes about half an inch. Over time, the infected area becomes inflamed, swollen, and painful, with the presence of more than one boil.
Following are the signs and symptoms of boils:
- Red, warm and swollen area
- Pain at the site of infection
- Itchiness
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Clogged skin pores
- Black or whiteheads
- Presence of abscess (pus)
- Clusters of boils at one place (carbuncle)
- Swollen lymph nodes around the boils
Risk Factors of Boils:
Boils are not related to a specific race or gender and can infect any person. But some people are more prone to this infection as compared to others.
Following are the aggravating factors of boils:
- A person with a weakened or compromised immune system
- Kidney failure
- Diabetes
- Hypogammaglobulinemia (An immune system disorder that is marked by low production of antibodies)
- Immunosuppressant medication including prednisolone, Deltasone, Medrol, or chemotherapy drugs
Complications:
The causative agent of boils, staphylococcus aureus, can lead to more serious complications such as MRSA (methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus).
Other possible complications of boils include:
- Cellulitis (A bacterial infection that is also caused by staphylococcus aureus)
- Impetigo (A bacterial infection that usually persists in children)
- Scarring or infection of the skin
- Bursting of the lump release filthy pus and may also lead to leakage of blood
- Infection of the hair follicles and sebaceous glands (Oil-producing glands)
- Worsening or severity of the infection
- Infection may spread to other areas of the body like the spinal cord, brain, kidneys, or lungs
- Recurrence of the infection
- Staphylococcus aureus may also produce some toxins that cause diseases like food poisoning, scalded skin syndrome, and shock syndrome
Timely treatment is necessary to avoid these complications.
When to see a doctor?
You should seek a consultancy of medical personnel if you are showing the symptoms of boils. Also, see a doctor if you have the following conditions:
- If you suscept a cluster of bumps at your face, armpits, anus, or spine
- If you are feeling unusual fatigue and fever
- Severe pain at the site of infection
- Recurring boils
- Your boils have not recovered in two weeks
- If the bump is growing bigger despite treatment (larger than 2 inches in size)
- If you are a patient of diabetes or taking immune-suppressing drugs and develop any symptoms of boils
Boils vs. Pimple:
Although boils may look like pimples in many aspects, they have some notable differences:
| Pimples | Boils |
| Small in size | Large in size |
| Form at one place and are localized | Can move away from the place of formation |
| Bacteria involved is Propionibacterium acnes | Bacteria involved is Staphylococcus aureus |
| Filled with pus | Filled with pus, characterized by fever and pain |
| Hormonal changes and over-production of oil | Clogged hair follicles can be a cause |
| Usually, heal on their own | Sometimes treatment is required |
Diagnosis :
A health care provider can diagnose boils by the physical examination of the site of infection. He may ask about the condition and observe the related parts of the body.
Usually, specialized laboratory tests are not required in this case. If it is really necessary, samples from the deeper tissues can be taken to confirm the infection.
Treatment of Boils:
Boils are not lethal. They can be easily treated once diagnosed. Both home remedies and allopathy drugs are available to overcome the infection.
· Home remedies:
Home remedies are the best way to treat minor and simple boils. The most suitable home remedy is heat application.
Procedure: Compress the boils with a warm cloth and soak in hot water. Hear of water will soften the area of the infection and also reduce the severity of the pain. Repeat the procedure thrice a day for three or four days.
Heat application works in two ways.
- There will be an increase in the flow of blood to the infectious site, thus allowing the body to fight the bacteria in a better way.
- An increase in heat denatures the membrane of bacteria and will kill them.
The pus will start to ooze out. Wash the place of infection with antibacterial soap and apply medical ointments to avoid inflammation.
· Medical treatments:
Antibiotics are the best medical treatment to treat carbuncle boils. There are many OTC (over-the-counter) ointments are available.
Antibiotics work by either inhibiting or killing the bacteria. Examples of these topical preparations include:
- Clindamycin
- Mupirocin
- Cephalexin
It is recommended to use medical options to avoid further spreading of the infection and complications. It is also advised not to take these medications without the consultancy of a professional medical person.
Prevention:
As explained earlier, boils are not linked to the hygiene of a person. On the other hand, they are also not completely preventable. Yet, you can decrease the chances of infection by following some simple steps.
Below is a list of these precautionary measures that you can adapt:
Avoid the infected person: As boils are contagious, a person with staph infection can be a good source of contamination. Avoid sharing things. Take special care if you are in a nearby area of such person.
Use of disinfectants: Clean all commonly used surfaces, including tables, sofas, doorknobs, and toilet seats, with suitable disinfectants. Wash your clothes regularly so that the infection may not spread. Adding bleach to the detergents can speed up the killing process of bacteria.
Use of hot water: Bacteria cannot persist under heat. Use hot water to wash pots and clothes. You can also utilize hot air for drying.
Take care of your hygiene: Antibacterial soaps kill the bacteria. Apply these soaps to wash hands and for baths regularly. Doing this can also lessen the infection of hair follicles and keep boils away.
Cover your boils: Do not touch the site of infection repeatedly. Do not pop the bumps. Use a clean and warm cloth to cover them. In case you touch the boils, wash your hands with antibacterial soap.



