What Are Sinuses? All you need to know about
Sinus: Defined:
A sinus is a void or cavity or hollow space within a bone or additional tissue, particularly one within the bones between your eyes, behind your cheekbones, and in your forehead.
They prepare mucus, which moistens the interior of your nose. That, in succession, assists conserving against dust, allergens, and contaminants. Healthy sinuses are packed with air.
Different Types of Paranasal Sinuses:
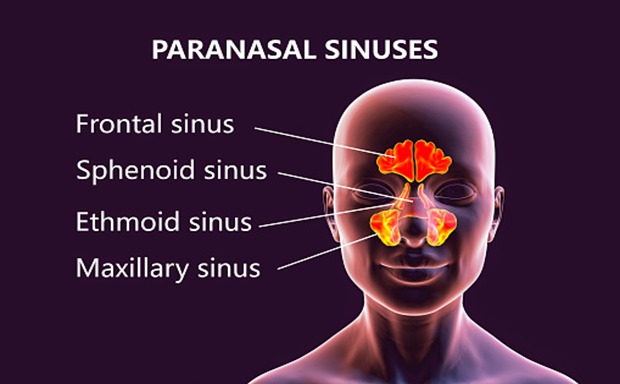
The four paired paranasal sinuses labeled for the skull bones in which they reside:
- Frontal sinuses: The right and left frontal sinuses are found near the middle of the deeper forehead (frontal bone) almost above each eye.
- The maxillary sinuses are placed in the cheekbones below the eyes.
- The ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes besides the upper nose
- The sphenoidal sinuses are behind the eyes and nose.
Drainage of the Paranasal Sinuses:
The paranasal sinuses are distributed per their drainage structures into
- Anterior sinuses group (maxillary, anterior ethmoid, and frontal sinuses) seeps into the middle meatus.
- The posterior sinuses group (posterior ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses) drips into the sphenoethmoidal recess.

Histology of the Paranasal Sinuses:
The nasal and paranasal cavities are covered with respiratory mucosa comprised of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
The lamina propria beneath encloses a heavy capillary system and is truly adhesive to the periosteum or perichondrium of adjoining bone or cartilage.
Sinuses Present at Birth:
Ethmoid sinus: around the area of the bridge of the nose.
Maxillary sinus: around the area of the cheeks.
Located inside the face, these sinuses are present at birth and continue to grow.
The function of the Paranasal Sinuses:
The apparent roles of the sinuses:
- Lessening the weight of the skull
- Diluting tension
- Humidifying and heating inspired air
- Soaking heat and protecting the brain
- Benefiting in sound resonance
- Giving mechanical rigidity
- Boosting the olfactory surface area
Disorders of the Paranasal Sinuses:
The diseases of the paranasal sinuses are as follows:
1-Sinusitis
What is Sinusitis?
Watery eyes, blocked nose and headache indicates inflammation of the sinuses which often feels like a bad cold.
Paranasal sinusitis is swelling of the mucous membranes in the paranasal sinuses. Sinusitis is a common disorder of the upper respiratory tract and may be acute or chronic.
- Acute sinusitis has rapid progress and mostly ends before 12 weeks. It responses well to therapy improve without complication and mostly is the result of a viral infection, e.g., a cold.
- Chronic paranasal sinusitis progresses slowly and is continuous. Those affected frequently have an anatomical aetiology, such as a curved nasal septum or polyps in the nose, which avoid the secretion to seep into the nose and throat.
Causes of sinusitis:
A cold, bacteria or virus invades the sinuses. The mucous membrane of the joining passageways surge.
The secretions produced in the sinuses cannot drain and collect in the sinuses making the ventilation of the cavities impossible.
Symptoms of sinusitis:
At first, the symptoms are similar to a cold: a blocked/runny nose inducing a headache.
Acute sinusitis can be indicated by a feeling of pressure or pain in the region of the forehead, cheeks and eyes. This tension increases when bending ahead or pressing.
Moreover, fever, exhaustion or swelling of the face might arise.
The symptoms of chronic sinusitis are less serious and generally painless. Yet, troubled breathing through the nose, stale discharge and impaired smell and taste are noted.
Diagnosis of sinusitis
A diagnosis mostly is made after merely patting the involved regions on the face.
Diagnosis may be assisted by paranasal sinus endoscopy, nasal discharge analysis, ultrasound or CT scan. Imaging methods are utilized to specify chronic sinusitis.
Treatment of Sinusitis:
For acute sinusitis, treatment with vapour inhalation and nasal sprays is helpful. Expectorants further are used.
For chronic sinusitis, nasal sprays with cortisone may be employed. The factors of chronic sinusitis may be relieved surgically (nasal polyps).
Paediatric Sinusitis:
Sinusitis in youngsters can differ from sinusitis in grown-ups. Furthermore, children present with cough, awful breath, grouchiness, poor energy, and bulging around the eyes, along with a thick yellow-green nasal or post-nasal drip.
Mostly, children are interpreted with a viral upper respiratory infection that will enhance by treatment for its symptoms, but antibiotics can be used in drastic cases of bacterial sinusitis.
Rarely where medication fails, surgery can be utilized as a productive procedure for doctoring sinus disorders in kids.
Your child’s sinuses are not completely mature until delayed in the teens. Though minor, the maxillary and ethmoid sinuses exist at birth.
Like sinusitis in grown-ups, paediatric sinusitis can be impossible to deduce because the symptoms may be induced by additional issues, such as a viral infection or allergy.
Sinuses Symptoms of Paediatric Sinusitis:
Following symptoms may demonstrate a sinus infection in children:
- A cold remaining further than 10 to 14 days
- Low- or even high-grade fever
- Thick yellow-green nasal drainage for a minimum of three days in a row
- Post-nasal drip, occasionally with irritated throat, cough, unpleasant breath, nauseousness
- Headache, usually in kids age six or former
- Grumpiness or exhaustion
- Bulging eyes
2-Paranasal Sinus Tumours
A membrane, bone, or nerve that line the region might induce a tumour. You might not doubt that a tumour is developing until it flares.
The earlier you get a diagnosis and begin therapy, the satisfactorily your possibilities of knocking the cancer are inclined to be.
Causes of Paranasal Sinus Tumours:
Not all paranasal sinus tumours have recognized causes, but some reasonable causes of paranasal sinus tumours:
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
- Industrial chemicals, wood, leather, flour, textile, nickel, chromium dust or radium exposed to the patients
- Smoking cigars/cigarettes
Symptoms of Paranasal Tumours:
Initial symptoms of paranasal sinus tumours are identical to symptoms of colds, so they're frequently missed:
- Obstructed sinuses, or congestion that never takes off
- Differences in your voice or breathing
- A lessened sensation of smell
- Headaches
- Numbness or anguish in your face, ears, or teeth
- Teeth loosen
- Pus dripping from your nose or postnasal drip
- Periodic nosebleeds
- Expansion on your face or palate
- Watery eyes
- Puffing eyes
- Altered vision
- Difficulty opening your mouth
Diagnosis of Paranasal Tumours:
A paranasal tumour is diagnosed in the following steps:
Medical History: A physician will first question you about your health.
Physical exam. The consultant will examine your eyes, ears, nose, mouth, face, neck, and throat for any signs.
Lab tests:
The following tests might be prescribed by your doctor:
- Endoscopy: test in which a slim tube with a small light and a video camera on the end is introduced into your sinuses to locate and size the tumour.
Your doctor might also order the following tests:
- Blood tests
- Imaging tests of your skull and chest such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI of the sinuses
- A biopsy, where a small tissue sample from the tumour is removed and checked in a lab for signs of cancer
Staging of Paranasal Tumours:
Fraction of the diagnosis procedure is known as staging. This informs your physician how progressed the tumour is and either it has invaded other parts of your body.
Staging assists your healthcare providers suggest the most appropriate treatment strategy for you.
The stage of your cancer relies on the location of the tumour, how much it has invaded into surrounding areas, whether it has dispersed to lymph nodes or additional parts of your body, and some added health characteristics.
The stages vary from I (initial stage) to IV (the most progressed). Stages for paranasal sinus tumours are:
- Stage I. The tumour is enclosed in the sinus and has not advanced.
- Stage II. The tumour has dispersed into additional areas of the sinus.
- Stage III. The tumour has advanced into the bone of the sinuses or the eye socket and may have dispersed to a lymph node.
- Stage IV. The tumour has moved further into the eye socket, into the brain, or into various parts of the skull and neck, and generally to more far-off parts of the body and may have a greater presence in the lymph nodes.
Sinuses Treatment of Paranasal Tumours:
The most popular procedure to cure a paranasal sinus tumour is a mixture of surgery and radiation treatment.
Surgery aims to clear as much of the tumour as feasible. If cancer has moved to lymph nodes; they will be cut out also.
Surgery will be designed to secure as much of your face and activity as feasible. Surgery can be complicated and may involve a group of experts.
The professionals who master in the ear, nose, and throat (ENT specialists or otorhinolaryngologists), neurosurgeons, and maxillofacial surgeons will together perform the surgery.
Radiation treatment may be provided before surgery to try to shrink the tumour. Or it may be given following surgery to remove any remaining tumour cells.
In the latter condition, it will generally begin various weeks after the surgery to permit adequate time for your body to improve.
Radiation might also be the basic procedure in some conditions, such as if a patient can’t have or does not want surgery.
Chemotherapy is the use of medications that damage cancer cells. A mixture of chemotherapy medicines or a mixture of chemotherapy and radiation, called chemoradiation might be the treatment.
Therapy will also involve pain supervision. Let your consultant or nurse know if you are suffering from pain so it can be better taken care of.
Sinuses Complications of Paranasal Tumours:
Paranasal sinus tumours and their therapy may direct to these complications:
- Damaging from surgery
- Long-term differences in vision, breathing, dialogue, eating, or swallowing, inflicted by the tumour or surgery
- Nerve damage that can impact feeling and action in your face, shoulder, or limbs
- Negative effects from radiation treatment, such as discomfort, nauseousness, problem eating, mouth sores, loss of teeth, and modifications in taste
- Cancer dissipates to additional parts of your body
People who are cured of paranasal sinus tumours should proceed to encounter yearly with their physician. If cancer retreats, it is most possible to occur in the first few years following therapy.



